Hooks 和 State Hook
hooks类型
目前React 16.7共有以下几种hooks,但是useListener还未公开使用
eexport type HookType =
| 'useState'
| 'useReducer'
| 'useContext'
| 'useRef'
| 'useEffect'
| 'useLayoutEffect'
| 'useCallback'
| 'useMemo'
| 'useImperativeHandle'
| 'useDebugValue'
| 'useListener';
hooks中的基本数据结构
- Update
- UpdateQueue
- Effect
- Hook
- 其他控制变量
1. Update
type Update<S, A> = {
expirationTime: ExpirationTime,//过期时间
suspenseConfig: null | SuspenseConfig,
action: A,//修改动作
eagerReducer: ((S, A) => S) | null,//下一个reducer
eagerState: S | null,//下一次的state
next: Update<S, A> | null,//下一个update
};
2. UpdateQueue
更新队列
type UpdateQueue<S, A> = {
last: Update<S, A> | null,
dispatch: (A => mixed) | null,
lastRenderedReducer: ((S, A) => S) | null,
lastRenderedState: S | null,
};
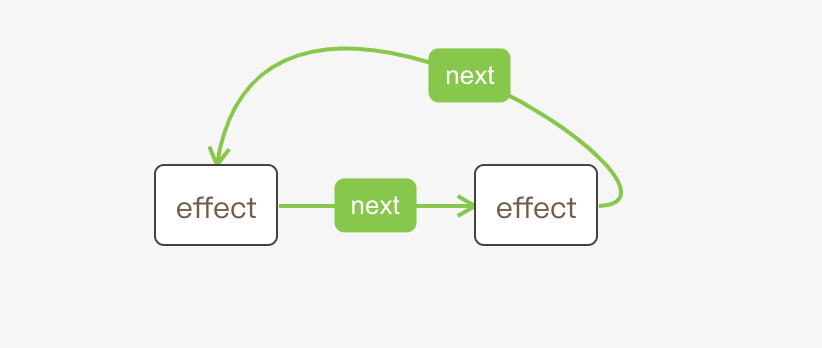
3. Effect
effect是一个循环链表结构
type Effect = {
tag: HookEffectTag,
create: () => (() => void) | void,//useEffect第一个参数
destroy: (() => void) | void,//useEffect返回的取消函数
deps: Array<mixed> | null,//依赖项
next: Effect,
};
- tag —— 一个二进制数字,它控制了 effect 节点的行为。
- create —— 绘制之后运行的回调函数。
- destroy —— 它是 create() 返回的回调函数,将会在初始渲染前运行。
- deps —— 一个集合,该集合中的值将会决定一个 effect 节点是否应该被销毁或者重新创建。
- next —— 它指向下一个定义在函数组件中的 effect 节点。
4. hook
export type Hook = {
memoizedState: any,
baseState: any, 传给 reducer 的状态对象。
baseUpdate: Update<any, any> | null,最近一次创建 baseState 的已发送的 action
queue: UpdateQueue<any, any> | null,已发送 action 组成的队列,等待传入 reducer。
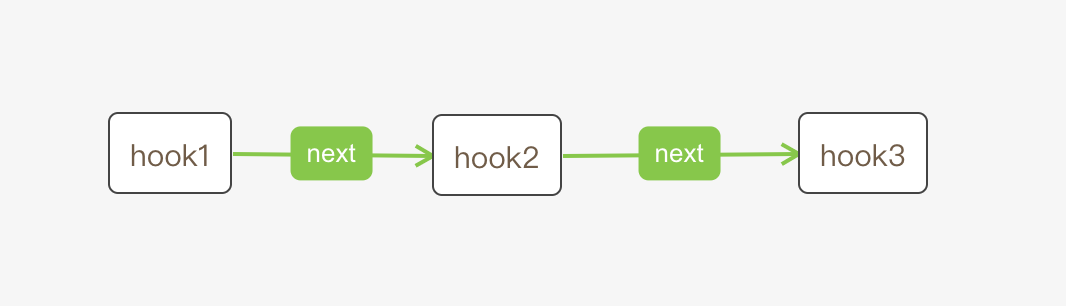
next: Hook | null,//下一个hook
};
 ;
;
在代码中hook是一个单链表,react维护两个hook相关到链表,一个是current hook list属于current fiber的,指针为currentHook和nextCurrentHook;一个是work-in-progress hook list,该list是属于work-in-progress fiber的,指针为firstWorkInProgressHook、workInProgressHook和nextWorkInProgressHook。
hook会保存到fiber的memoizedState属性上
let currentHook = null; // 指向current fiber中当前的hook
let nextCurrentHook = null; // 指向current fiber中下一个hook
let firstWorkInProgressHook = null; // 指向work-in-progress fiber第一个hook
let workInProgressHook = null; // 指向work-in-progress fiber当前hook
let nextWorkInProgressHook = null; // 指向work-in-progress fiber下一个hook
react还维护着两个与hook类型有关的列表,列表确保在每次渲染的时候都以相同的顺序调用hooks。
let hookTypesDev = null; // 存储初始渲染(mount)时hook的顺序
let hookTypesUpdateIndexDev = -1; // 后续渲染(update)时使用
hook的mount阶段和update阶段
在mount阶段,初始化新的hook,在update阶段,将current fiber的hook克隆到work-in-progress fiber中。
function mountWorkInProgressHook(): Hook {
const hook: Hook = {
memoizedState: null,
baseState: null,
queue: null,
baseUpdate: null,
next: null,
};
if (workInProgressHook === null) {
// 如果之前没有list中hook,则是第一个hook
firstWorkInProgressHook = workInProgressHook = hook;
} else {
// 否则,则向链表中增加hook
workInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next = hook;
}
//返回新增的hook
return workInProgressHook;
}
function updateWorkInProgressHook(): Hook {
//这个方法用于更新和render阶段触发的重新渲染
if (nextWorkInProgressHook !== null) {
// 已经存在 work-in-progress的话就复用它.
workInProgressHook = nextWorkInProgressHook;
nextWorkInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next;
currentHook = nextCurrentHook;
nextCurrentHook = currentHook !== null ? currentHook.next : null;
} else {
// 从 current hook克隆.
currentHook = nextCurrentHook;
const newHook: Hook = {
memoizedState: currentHook.memoizedState,
baseState: currentHook.baseState,
queue: currentHook.queue,
baseUpdate: currentHook.baseUpdate,
next: null,
};
if (workInProgressHook === null) {
// This is the first hook in the list.
workInProgressHook = firstWorkInProgressHook = newHook;
} else {
// Append to the end of the list.
workInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next = newHook;
}
nextCurrentHook = currentHook.next;
}
return workInProgressHook;
}
在React中hooks的mount阶段和update阶段对应的处理方法很多是不同的,比如
HooksDispatcherOnMount ,HooksDispatcherOnUpdate,这两个方法中useState,useEffect等方法实现不逻辑一样,分别处理mount和update阶段的任务。
会通过nextCurrentHook区分这两个阶段
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current =
nextCurrentHook === null
? HooksDispatcherOnMount
: HooksDispatcherOnUpdate;
hooks的调用过程
hooks是在函数组件中使用的,所以需要关注函数组件的调用过程及使用的方法。
重点关注renderWithHooks 方法,renderWithHooks函数就是处理各种hooks逻辑的核心部分
mount过程执行mountIndeterminateComponent,renderWithHooks的第一个参数current=null;
update过程中执行updateFunctionComponent,renderWithHooks的第一个参数current为workInProgress.alternate
renderWithHooks(
current: Fiber | null, //当前的fiber结点
workInProgress: Fiber,
Component: any, //jsx中用<>调用的函数
props: any,
refOrContext: any,
nextRenderExpirationTime: ExpirationTime, //过期时间
): any
renderWithHooks的主要功能是
// currentlyRenderingFiber$1指向workInProgress
currentlyRenderingFiber$1 = workInProgress;
//从memoizedState中取出hooks
nextCurrentHook = current !== null ? current.memoizedState : null;
//用nextCurrentHook的值来区分mount和update,设置不同的dispatcher
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current =
nextCurrentHook === null
? HooksDispatcherOnMount
: HooksDispatcherOnUpdate;
//执行传入的type函数,此时已经有了新的dispatcher,在调用Component时就可以拿到新的对象
let children = Component(props, refOrContext);
//重置为ContextOnlyDispatcher
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current = ContextOnlyDispatcher;
// 更新memoizedState和updateQueue
let renderedWork = currentlyRenderingFiber$1;
renderedWork.memoizedState = firstWorkInProgressHook;
renderedWork.expirationTime = remainingExpirationTime;
renderedWork.updateQueue = componentUpdateQueue;
renderedWork.effectTag |= sideEffectTag;
//重置各种变量
renderExpirationTime = NoWork;
currentlyRenderingFiber$1 = null;
currentHook = null;
nextCurrentHook = null;
firstWorkInProgressHook = null;
workInProgressHook = null;
nextWorkInProgressHook = null;
remainingExpirationTime = NoWork;
componentUpdateQueue = null;
sideEffectTag = 0;
return children;
当执行Component(props, refOrContext)的时候就会调用函数组件中的useState等方法处理hooks。
在这个例子中会依次调用hooks方法,并生成一个hooks链表,保存到 当前fiber的memoizedState中,副作用effect会额外保存一份到fiber的updateQueue中,并标记当前fiber的effectTag。
以useState为例说一下大致流程
const Hello = () => {
const [count, setCount] = React.useState(0);
const [name, setName] = React.useState("test");
const onClick = ()=>{
setCount(1);
setName('hello world');
}
React.useEffect(() => {
document.title = `You clicked ${count} times`;
},[count]);
React.useEffect(() => {
fetch('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/1')
.then(response => response.json())
.then(json => console.log(json))
},[name]);
return (
<React.Fragment>
<div style={{'backgroundColor':'red','height':100}} onClick={onClick}>click me </div>
<p>我是{name}</p>
</React.Fragment>
);
}
hooks初始化
创建一个新的hook,初始化state, 并绑定触发器
初始化阶段ReactCurrentDispatcher.current 会指向HooksDispatcherOnMount 对象
const HooksDispatcherOnMount: Dispatcher = {
/** 省略其它Hooks **/
useState: mountState,
};
mountState
function mountState<S>(
initialState: (() => S) | S,
): [S, Dispatch<BasicStateAction<S>>] {
//创建一个hook,改变workInProgressHook指针指向
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
//initialState是函数就调用它
if (typeof initialState === 'function') {
initialState = initialState();
}
//state初始化
hook.memoizedState = hook.baseState = initialState;
//queue初始化
const queue = (hook.queue = {
last: null,//最近的一次更新
dispatch: null,
lastRenderedReducer: basicStateReducer,// useState使用基础reducer
lastRenderedState: (initialState: any),
});
// 触发器绑定当前fiber和queue
const dispatch: Dispatch<
BasicStateAction<S>,
> = (queue.dispatch = (dispatchAction.bind(
null,
((currentlyRenderingFiber: any): Fiber),
queue,
): any));
// 返回初始state和触发器
return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch];
}
可以看到dispatch就是dispatchAction绑定了对应的Fiber和queue这两个参数。
function basicStateReducer<S>(state: S, action: BasicStateAction<S>): S {
return typeof action === 'function' ? action(state) : action;
}
dispatchAction
function dispatchAction<S, A>(
fiber: Fiber,
queue: UpdateQueue<S, A>,
action: A,
) {
const alternate = fiber.alternate;
if (
fiber === currentlyRenderingFiber ||
(alternate !== null && alternate === currentlyRenderingFiber)
) {
//这是一个render阶段的update,先保存在一个懒创建的map中,在render阶段结束之后在重启改任务,将其应用在work-in-progress hook上
didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdate = true;
//创建update
const update: Update<S, A> = {
expirationTime: renderExpirationTime,
suspenseConfig: null,
action,
eagerReducer: null,
eagerState: null,
next: null,
};
//renderPhaseUpdates这个Map以每个Hook的queue为key。
if (renderPhaseUpdates === null) {
renderPhaseUpdates = new Map();
}
const firstRenderPhaseUpdate = renderPhaseUpdates.get(queue);
if (firstRenderPhaseUpdate === undefined) {
renderPhaseUpdates.set(queue, update);
} else {
// Append the update to the end of the list.
let lastRenderPhaseUpdate = firstRenderPhaseUpdate;
while (lastRenderPhaseUpdate.next !== null) {
lastRenderPhaseUpdate = lastRenderPhaseUpdate.next;
}
lastRenderPhaseUpdate.next = update;
}
} else {
if (revertPassiveEffectsChange) {
flushPassiveEffects();
}
const currentTime = requestCurrentTime();
const suspenseConfig = requestCurrentSuspenseConfig();
const expirationTime = computeExpirationForFiber(
currentTime,
fiber,
suspenseConfig,
);
//创建update
const update: Update<S, A> = {
expirationTime,
suspenseConfig,
action,
eagerReducer: null,
eagerState: null,
next: null,
};
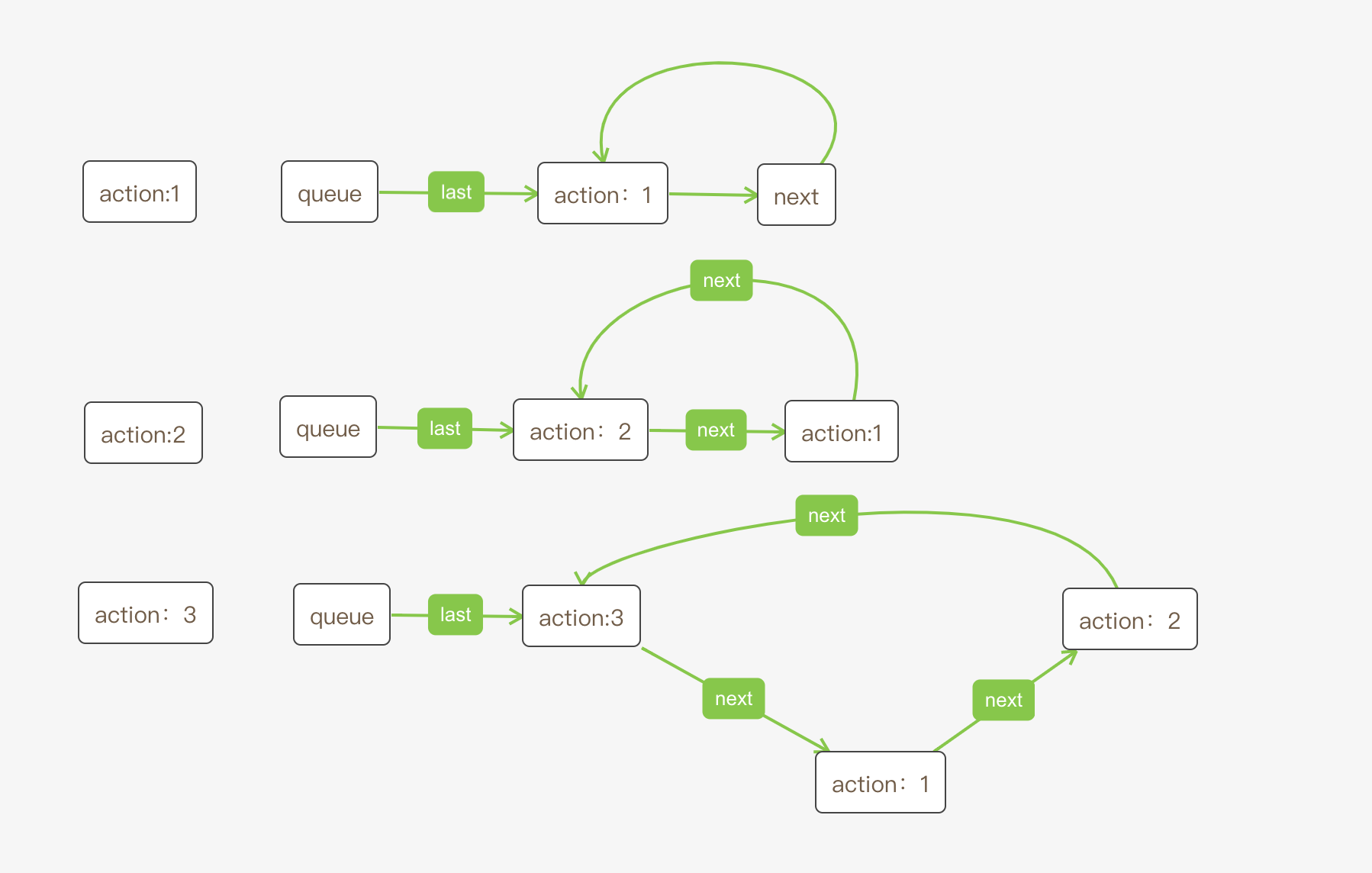
、 //将update添加到list的末尾
const last = queue.last;
if (last === null) {
//这是第一个update,要创建一个循环链表
update.next = update;
} else {
const first = last.next;
if (first !== null) {
// Still circular.
update.next = first;
}
last.next = update;
}
//last指向最新的一次update,last.next指向第一次更新
queue.last = update;
if (
fiber.expirationTime === NoWork &&
(alternate === null || alternate.expirationTime === NoWork)
) {
// queue 是空的,意味着可以在进入render阶段之前就计算下一个state,如果新的state和当前的state相同,可以熔断。
const lastRenderedReducer = queue.lastRenderedReducer;
if (lastRenderedReducer !== null) {
let prevDispatcher;
if (__DEV__) {
prevDispatcher = ReactCurrentDispatcher.current;
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current = InvalidNestedHooksDispatcherOnUpdateInDEV;
}
try {
const currentState: S = (queue.lastRenderedState: any);
const eagerState = lastRenderedReducer(currentState, action);
//保存计算出来的新state和reducer,如果reducer没有变化,在render阶段就可以使用刚计算出来的state,不需要再次调用reducer
update.eagerReducer = lastRenderedReducer;
update.eagerState = eagerState;
if (is(eagerState, currentState)) {
// state没有变化,可以熔断,防止重复渲染
return;
}
} catch (error) {
// Suppress the error. It will throw again in the render phase.
} finally {
if (__DEV__) {
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current = prevDispatcher;
}
}
}
}
scheduleWork(fiber, expirationTime);
}
}
当连续三次调用同一个dispatch时,queue的链表关系如下,如
setCount(1);
setCount(2);
setCount(3);
hook 更新
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current 会指向HooksDispatcherOnUpdate 对象
确保hook的顺序问题
hookTypesUpdateIndexDev 更新阶段初始化为0
function updateHookTypesDev() {
if (__DEV__) {
const hookName = ((currentHookNameInDev: any): HookType);
if (hookTypesDev !== null) {
hookTypesUpdateIndexDev++;
if (hookTypesDev[hookTypesUpdateIndexDev] !== hookName) {
warnOnHookMismatchInDev(hookName);
}
}
}
}
调用updateState
useState底层是useReducer,所以在更新时的流程(即重渲染组件后)是调用updateReducer的。
function updateState(initialState) {
return updateReducer(basicStateReducer, initialState);
}
function updateReducer<S, I, A>(
reducer: (S, A) => S,
initialArg: I,
init?: I => S,
): [S, Dispatch<A>] {
//获取当前hook
const hook = updateWorkInProgressHook();
const queue = hook.queue;
invariant(
queue !== null,
'Should have a queue. This is likely a bug in React. Please file an issue.',
);
queue.lastRenderedReducer = reducer;
if (numberOfReRenders > 0) {
//重新render,将新render阶段的update添加到以前的work-in-progress hook
const dispatch: Dispatch<A> = (queue.dispatch: any);
//此变量在dispatchAction中设置过,调用我们的setCount函数会调用dispatchAction
if (renderPhaseUpdates !== null) {
//render阶段的更新被存储在map中,是一个链表
const firstRenderPhaseUpdate = renderPhaseUpdates.get(queue);
if (firstRenderPhaseUpdate !== undefined) {
renderPhaseUpdates.delete(queue);
let newState = hook.memoizedState;
let update = firstRenderPhaseUpdate;
do {
const action = update.action;
newState = reducer(newState, action);
update = update.next;
} while (update !== null);
// Mark that the fiber performed work, but only if the new state is
// different from the current state.
if (!is(newState, hook.memoizedState)) {
markWorkInProgressReceivedUpdate();
}
hook.memoizedState = newState;
// Don't persist the state accumlated from the render phase updates to
// the base state unless the queue is empty.
if (hook.baseUpdate === queue.last) {
hook.baseState = newState;
}
queue.lastRenderedState = newState;
return [newState, dispatch];
}
}
return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch];
}
// 整个queue中的最后一个update
const last = queue.last;
// 最后一个update是基本状态
const baseUpdate = hook.baseUpdate;
const baseState = hook.baseState;
// 找到第一个未处理的update.
let first;
if (baseUpdate !== null) {
if (last !== null) {
//由于queue是一个循环链表,`queue.last.next = queue.first` 一旦第一个update提交了,baseUpdate就不再是空的,此时设置last.next = null,意味着不用处理以前处理过的update
last.next = null;
}
//由于是循环链表和结构共享,baseUpdate.next指向的是最新的update
first = baseUpdate.next;
} else {
first = last !== null ? last.next : null;
}
if (first !== null) {
let newState = baseState;
let newBaseState = null;
let newBaseUpdate = null;
let prevUpdate = baseUpdate;
let update = first;
let didSkip = false;
do {
const updateExpirationTime = update.expirationTime;
if (updateExpirationTime < renderExpirationTime) {
// Priority is insufficient. Skip this update. If this is the first
// skipped update, the previous update/state is the new base
// update/state.
//优先级不够,就跳过此update,如果这是第一个跳过的update,那么以前的update/state,就是新的基本 update/state.
if (!didSkip) {
didSkip = true;
newBaseUpdate = prevUpdate;
newBaseState = newState;
}
// Update the remaining priority in the queue.
if (updateExpirationTime > remainingExpirationTime) {
remainingExpirationTime = updateExpirationTime;
}
} else {
// 优先级足够
markRenderEventTimeAndConfig(
updateExpirationTime,
update.suspenseConfig,
);
// 处理update
if (update.eagerReducer === reducer) {
//如果这个update被处理过,它的reducer和当前的reducer是匹配的,可以使用处理过的state
newState = ((update.eagerState: any): S);
} else {
//重新计算state
const action = update.action;
newState = reducer(newState, action);
}
}
prevUpdate = update;
update = update.next;
} while (update !== null && update !== first);
//未跳过任何update
if (!didSkip) {
newBaseUpdate = prevUpdate;
newBaseState = newState;
}
if (!is(newState, hook.memoizedState)) {
markWorkInProgressReceivedUpdate();
}
hook.memoizedState = newState;
hook.baseUpdate = newBaseUpdate;
hook.baseState = newBaseState;
queue.lastRenderedState = newState;
}
const dispatch: Dispatch<A> = (queue.dispatch: any);
return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch];
}
总结
单个hook的更新行为全都挂在Hooks.queue下,需要维护好Hooks.queue
- 初始化queue - mountState
- 维护queue - dispatchAction
更新queue - updateReducer
当第一次调用[count, setCount] = useState(0)时,创建一个queue
- 每一次调用setCount(x),就dispach一个内容为x的action(action的表现为:将count设为x),action存储在queue中。
- 这些action最终在updateReducer中被调用,更新到memoizedState上,使我们能够获取到最新的state值。